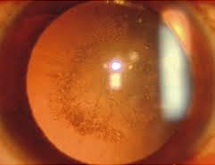
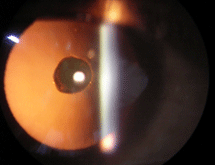
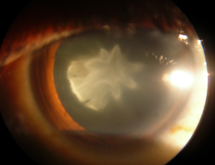
1. Age related cataract 'Most common type of cataract . It can present in 3 forms'
a) Cataracts that affect the center of the lens (nuclear cataracts). A nuclear cataract may at first cause you to become more nearsighted or even experience a temporary improvement in your reading vision. But with time, the lens gradually turns more densely yellow and further clouds your vision.As the cataract slowly progresses, the lens may even turn brown. Advanced yellowing or browning of the lens can lead to difficulty distinguishing between shades of color.
 Nuclear sclerosis grade 1
Nuclear sclerosis grade 1
 Nuclear sclerosis grade 2
Nuclear sclerosis grade 2
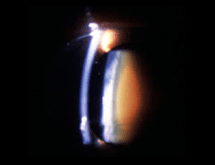 Nuclear sclerosis grade 3
Nuclear sclerosis grade 3
 Nuclear sclerosis grade 4
Nuclear sclerosis grade 4
b) Cataracts that affect the edges of the lens (cortical cataracts). A cortical cataract begins as whitish, wedge-shaped opacities or streaks on the outer edge of the lens cortex. As it slowly progresses, the streaks extend to the center and interfere with light passing through the center of the lens. People with cortical cataracts often experience problems with glare.
c) Cataracts that affect the back of the lens (posterior subcapsular cataracts). A posterior subcapsular cataract starts as a small, opaque area that usually forms near the back of the lens, right in the path of light on its way to the retina. A posterior subcapsular cataract often interferes with your reading vision, reduces your vision in bright light, and causes glare or halos around lights at night.
2. Congenital and developmental cataract
"Some children are born with cataracts. In some cases, the inherited cataract is not significant enough to affect vision. If significant, however, the cataract should be removed in order to avoid vision problems, such as strabismus or amblyopia. Posterior polar cataract" Posterior polar cataracts are characterized by well-demarcated white opacities in the center of the posterior capsule. These opacities often project forward as cylinders penetrating into the posterior lens cortex.
Most posterior polar cataracts are asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic. However, over time posterior subcapsular (PSC) opacities may form around the posterior polar opacity. As the PSC progresses, vision may be severely affected. Posterior polar cataracts pose a unique challenge for cataract surgery. The rate of posterior capsular rupture is significantly higher in these cases. The posterior capsule is weakened around the posterior polar opacity and in some cases there may even be a defect in the capsule.
3. Secondary Cataracts
Cataracts can sometimes develop after undergoing eye surgery, such as surgery for glaucoma or retinal surgery. Patients with diabetes sometimes develop cataracts earlier than normal. Also, patients who are taking steroids for an extended period of time may develop cataracts
4. Traumatic Cataract
A traumatic cataract can occur following both blunt and penetrating eye injuries as well as after electrocution, chemical burns, and exposure to radiation